
- RFQ
- BOM
-
Contact Us
Tel: +86-0755-83501315
Email: sales@sic-components.com
- Chinese
- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur
Voltage - Feedback Amplifiers: A Comprehensive Overview
1. Introduction
Voltage - feedback amplifiers (VFAs) stand as fundamental building blocks within the realm of electronic circuits, playing a pivotal role in numerous applications. Their significance lies in their ability to accurately amplify and manipulate voltage signals, ensuring the reliable operation of a wide range of electronic devices. From audio systems that bring our favorite music to life with high - fidelity sound reproduction to complex communication systems that enable seamless data transmission, and even in precision - oriented scientific and medical equipment, voltage - feedback amplifiers are indispensable components.
2. Principle of Operation
2.1 The Concept of Feedback
At the heart of a voltage - feedback amplifier is the principle of feedback. A fraction of the output voltage is “fed back” to the amplifier's input. This feedback mechanism serves as a self - adjustment tool for the amplifier. By comparing the input signal with the feedback signal, the amplifier can make real - time corrections to its output, thereby minimizing errors and producing a more stable and predictable output signal. There are two types of feedback: positive and negative.
2.2 Negative Feedback in VFAs
Negative feedback is the workhorse in voltage - feedback amplifiers, offering a plethora of benefits. When a portion of the output signal is fed back to the input in an out - of - phase manner, it has a profound impact on the amplifier's performance.
Enhanced Stability: One of the primary advantages of negative feedback is its ability to improve the amplifier's stability. By reducing the overall gain of the amplifier, it makes the system less prone to oscillations and fluctuations. In a practical sense, this means that the amplifier can operate more reliably over a wider range of input signals and environmental conditions. For example, in an audio amplifier, stability ensures that the sound output remains consistent without sudden changes in volume or distortion, even if the input signal from a music source varies slightly.
Distortion Reduction: Negative feedback also plays a crucial role in minimizing non - linear distortion. In an amplifier, without proper feedback, the gain can be highly dependent on the operating point of the transistors or other active components. This can lead to distortion, where the output signal does not faithfully represent the input signal. Negative feedback counteracts this by making the gain less sensitive to the transistor's operating point. As a result, the output signal more accurately replicates the input signal, which is essential for applications such as high - quality audio reproduction, where any distortion can degrade the listening experience.
Increased Bandwidth: Another significant benefit of negative feedback is the expansion of the amplifier's bandwidth. The bandwidth of an amplifier refers to the range of frequencies over which it can effectively amplify the input signal. Negative feedback allows the amplifier to handle a broader spectrum of frequencies, enabling it to process signals with more complex frequency content. For instance, in a communication system that needs to transmit and receive a wide range of data - carrying frequencies, a voltage - feedback amplifier with increased bandwidth can ensure that all the signals are amplified accurately without loss of information.
2.3 Positive Feedback in VFAs
While negative feedback is more commonly used, positive feedback also has its applications in voltage - feedback amplifiers. In positive feedback, a portion of the output signal is fed back to the input in - phase with the input signal. This has the effect of increasing the gain of the amplifier. In some applications, such as oscillator circuits, a high gain is desirable to generate a continuous oscillating signal. Positive feedback can cause the amplifier to quickly reach a state of saturation or maximum output. However, it's important to note that positive feedback also comes with challenges. Since it amplifies even small changes in the input signal, it can lead to increased distortion and instability if not carefully controlled. In an oscillator circuit, for example, precise control of positive feedback is necessary to generate a stable, sinusoidal output signal. If the feedback is too strong, the oscillator may produce a distorted or erratic waveform.
3. Inner Workings of a Voltage - Feedback Amplifier
3.1 Amplifier Section
The amplifier section of a voltage - feedback amplifier is where the initial signal amplification takes place. It typically consists of a differential amplifier and a power amplifier.
Differential Amplifier: The differential amplifier is responsible for amplifying the difference between the input signal and the feedback signal. It plays a crucial role in determining the amplifier's ability to reject common - mode signals (signals that are present equally on both inputs). By amplifying only the difference between the two inputs, the differential amplifier helps to enhance the signal - to - noise ratio of the overall system. For example, in a sensor application where the input signal may be accompanied by some background noise, the differential amplifier can effectively separate the desired signal from the noise, ensuring that only the relevant information is further processed.
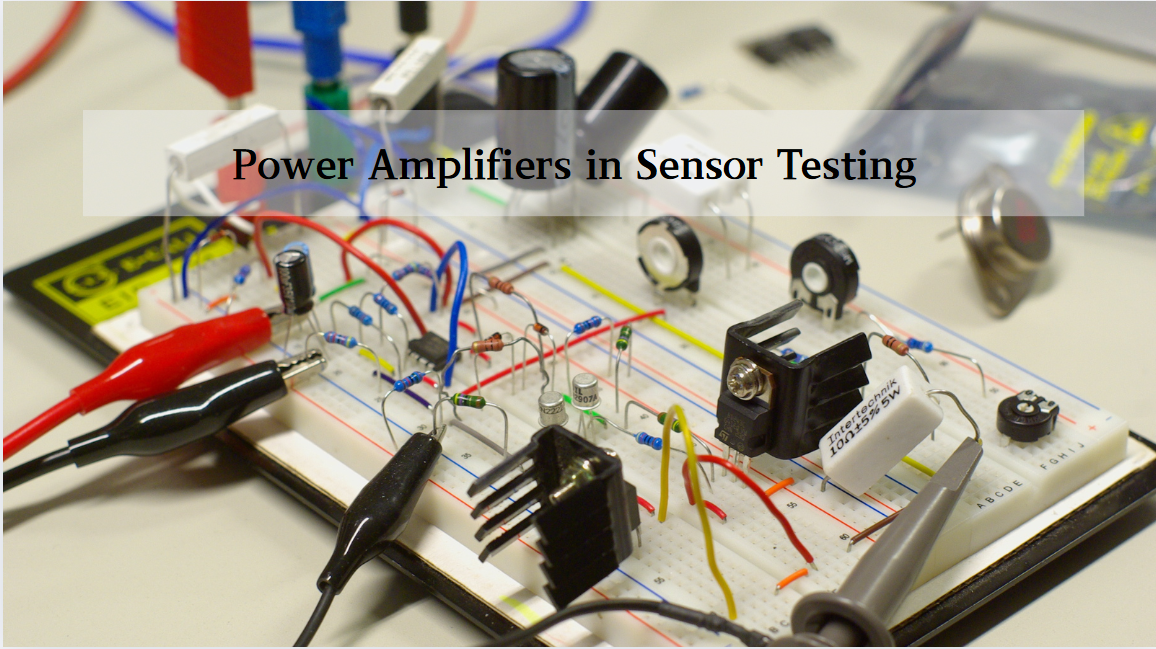
Power Amplifier: After the differential amplifier has amplified the difference signal, the power amplifier takes over. Its role is to further amplify this signal to the desired output level. The power amplifier is designed to handle the power requirements of the load connected to the amplifier. In an audio amplifier, for instance, the power amplifier provides the necessary power to drive speakers, ensuring that the sound is loud and clear. The power amplifier needs to be carefully designed to avoid distortion and efficiently transfer power to the load.
3.2 Feedback Network
The feedback network is an integral part of the voltage - feedback amplifier, as it determines the proportion of the output signal that is returned to the input. In most cases, the feedback network is a simple resistor network. By carefully selecting the values of the resistors in the feedback network, engineers can control the amount of feedback and, consequently, the overall gain of the voltage - feedback amplifier. For example, in a basic inverting amplifier configuration, the ratio of the feedback resistor to the input resistor determines the gain of the amplifier. If the feedback resistor has a higher value compared to the input resistor, the amplifier will have a higher gain. The feedback network also affects other characteristics of the amplifier, such as its input and output impedance. By adjusting the feedback network, engineers can optimize these parameters to match the requirements of the specific application.
4. Applications of Voltage - Feedback Amplifiers
4.1 Audio Systems
Voltage - feedback amplifiers are widely used in audio systems to ensure high - quality sound reproduction. In an audio amplifier, the voltage - feedback amplifier helps to maintain the integrity of the sound signal. By reducing distortion and preventing saturation, it ensures that the music or other audio content is reproduced as faithfully as possible. For example, in a high - end home audio system, the voltage - feedback amplifier in the power amplifier stage drives the speakers with a clean and powerful signal, allowing the listener to enjoy the nuances of the music. In a headphone amplifier, the voltage - feedback amplifier provides the necessary amplification to drive the headphones, delivering clear and detailed sound directly to the user's ears.
4.2 Telecommunication Systems
In telecommunication systems, voltage - feedback amplifiers are used in various signal - processing applications. They are employed in the design of filters, which are used to select or reject specific frequencies in a signal. For example, in a radio receiver, a voltage - feedback amplifier - based filter can be used to isolate the desired radio frequency signal from the background noise and other unwanted signals. Voltage - feedback amplifiers are also used in oscillator circuits in telecommunication systems. Oscillators generate the carrier frequencies used for signal transmission. The stability and accuracy of the oscillator are crucial for reliable communication. Voltage - feedback amplifiers with their ability to provide stable gain and precise signal control are well - suited for this application. Additionally, in signal amplifiers within telecommunication systems, voltage - feedback amplifiers ensure that the signals are amplified to the appropriate level for further processing or transmission.
4.3 Scientific and Medical Equipment
In scientific and medical equipment, where precision is of utmost importance, voltage - feedback amplifiers are often used. In a laboratory instrument such as an oscilloscope, which is used to measure and display electrical signals, voltage - feedback amplifiers are used to amplify the input signals to a level that can be accurately measured and displayed. In medical equipment like electrocardiogram (ECG) machines, voltage - feedback amplifiers play a crucial role in amplifying the weak electrical signals generated by the heart. These signals are then used to diagnose various heart conditions. The stability and low - distortion characteristics of voltage - feedback amplifiers are essential in medical applications to ensure accurate signal processing and reliable diagnosis. In other medical imaging equipment, such as ultrasound machines, voltage - feedback amplifiers are used to amplify the received echo signals, enabling clear imaging of internal organs.
5. Conclusion
Voltage - feedback amplifiers are essential components in the world of electronics. Their ability to use feedback to control signal amplification makes them highly versatile and reliable. By understanding their principles of operation, inner workings, and applications, engineers can design and optimize electronic circuits to meet the specific requirements of various industries. Whether it's enhancing the sound quality in audio systems, enabling seamless communication in telecommunication networks, or providing accurate signal processing in scientific and medical equipment, voltage - feedback amplifiers continue to be a cornerstone technology in the ever - evolving field of electronics. As technology advances, further improvements in voltage - feedback amplifier design are expected, leading to even more efficient and high - performance electronic devices.
https://www.sic-components.com/amplifierscategory-1
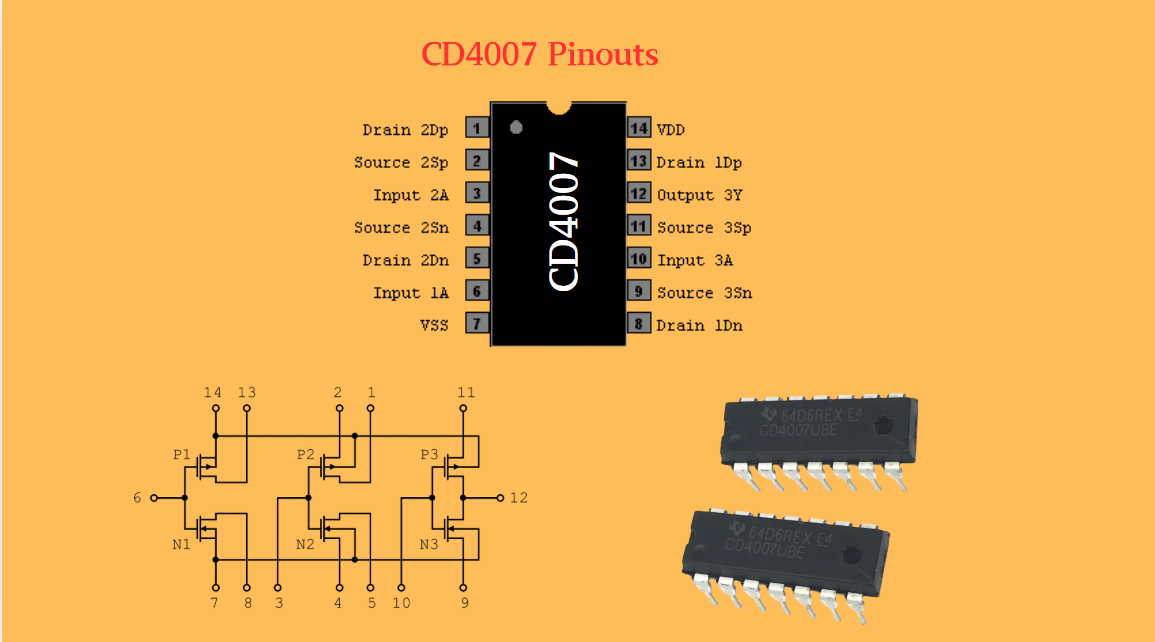
Hot Products
View MoreRelated Blogs

2000+
Daily average RFQ Volume

30,000,000
Standard Product Unit

2800+
Worldwide Manufacturers

15,000 m2
In-stock Warehouse






















 Wishlist (0 Items)
Wishlist (0 Items) 