
- RFQ
- BOM
-
Contact Us
Tel: +86-0755-83501315
Email: sales@sic-components.com
- Chinese
- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur
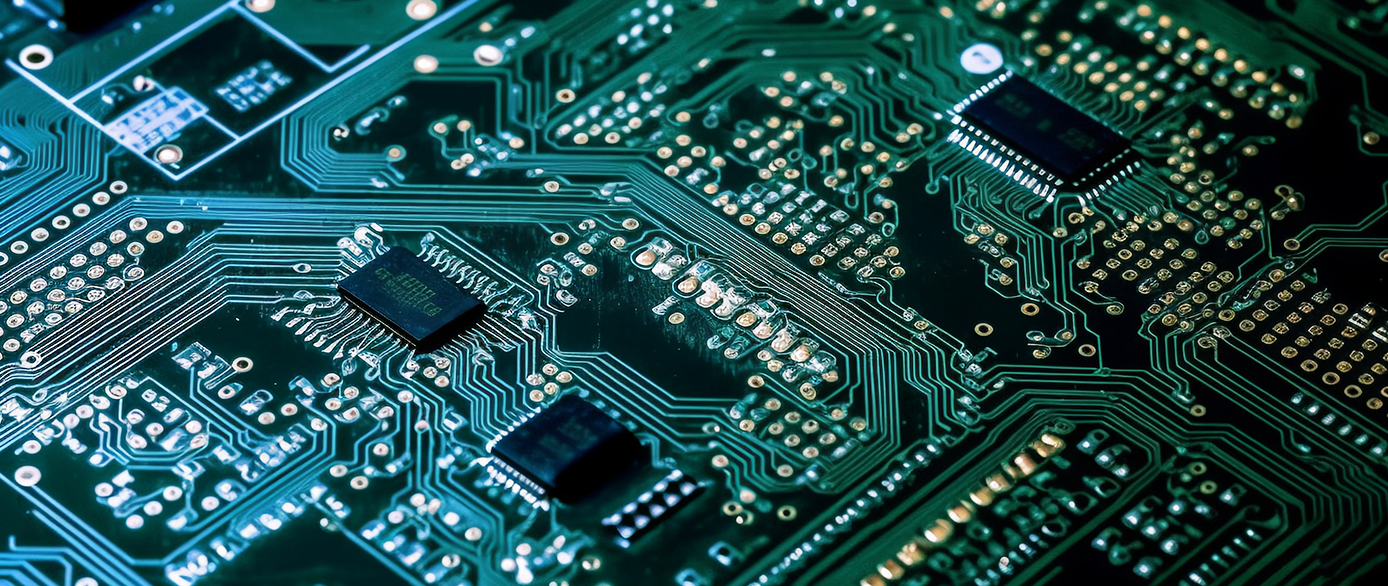
Guide to Understanding and Using SMD Connectors in Industrial Applications
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial electronics, staying abreast of the latest technological advancements is crucial for companies aiming to remain competitive. Among the key components driving innovation in this field are Surface Mount Device (SMD) connectors. These unassuming yet essential elements play a pivotal role in numerous industrial applications, and a comprehensive understanding of their features, types, applications, selection criteria, and potential issues is vital for maximizing their benefits.
What Are SMD Connectors?
SMD connectors are specialized electrical connectors designed for use with printed circuit boards (PCBs) and surface-mount devices (SMDs). Unlike traditional through-hole connectors, which require holes to be drilled through the PCB for component insertion, SMD connectors are soldered directly onto the surface of the board. This surface-mount technology (SMT) offers several advantages, including reduced board space requirements, improved manufacturing efficiency, and enhanced electrical performance.
The Evolution of SMD Technology
It’s fascinating to think that while SMD components have their roots in the 1960s, it wasn’t until the vibrant tech boom of the 1980s that they truly found their place in mainstream electronics. As the demand for smaller, more portable electronic devices grew, the limitations of traditional through-hole components became evident. Their long leads and larger sizes were becoming less practical for the evolving needs of the industry. SMD technology emerged in response, offering a more compact and efficient solution that would shape the future of electronics.
Key Characteristics of SMD Components
Size: One of the first things you’ll notice about SMD components? Their size. They’re impressively compact compared to traditional components. This isn’t just for aesthetics; it allows for a much denser arrangement on a PCB.
Flexibility: Their design allows SMD components to be placed on both sides of a PCB, facilitating more intricate circuit designs.
Durability: With fewer external leads and a direct mount to the PCB, SMD components tend to be more robust and reliable.
Types of SMD Connectors
The market offers a diverse range of SMD connectors, each tailored to specific application requirements. Here are some of the most common types:
DIP (Dual In-Line Package) Connectors: These are among the most widely used SMD connectors in electronic applications. They feature two rows of pins that are soldered onto the PCB, providing a reliable connection for a variety of components.
SIP (Single In-Line Package) Connectors: Similar to DIP connectors but with a single row of pins, SIP connectors are ideal for high-density applications where space is at a premium.
PGA (Pin Grid Array) Connectors: PGA connectors consist of a grid of pins that are soldered to the PCB, offering a high pin count and excellent electrical performance. They are commonly used in applications requiring high bandwidth and signal integrity.
BGA (Ball Grid Array) Connectors: BGA connectors feature a grid of balls on the underside of the package, which are soldered to the PCB. This design provides a low-profile, high-density connection solution, making them suitable for applications such as mobile devices and high-performance computing.
LGA (Land Grid Array) Connectors: LGA connectors use a grid of land contacts instead of pins, providing a more reliable and durable connection. They are often used in high-speed applications where signal integrity is critical.
QFP (Quad Flat Package) Connectors: QFP connectors have a square or rectangular shape with leads extending from all four sides. They are commonly used in microcontrollers and other integrated circuits, offering a good balance between performance and cost.
Applications of SMD Connectors in Industrial Machines
The versatility of SMD connectors makes them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. Here are some examples of how they are used in different industries:
Medical Devices: SMD connectors are used in medical equipment such as patient monitors, diagnostic devices, and surgical instruments. They provide a reliable and compact connection solution, ensuring the accurate transmission of data and signals.
Manufacturing Equipment: In manufacturing plants, SMD connectors are used in automated machinery, robotics, and control systems. They enable the seamless integration of various components, facilitating efficient production processes.
Telecommunications Equipment: SMD connectors play a crucial role in telecommunications infrastructure, including cell towers, base stations, and network switches. They provide high-speed, reliable connections for data transmission and signal processing.
Automotive Applications: SMD connectors are used in automotive electronics, such as engine control units, infotainment systems, and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). They offer a compact and robust solution for connecting various components in harsh automotive environments.
Aerospace and Defense: In aerospace and defense applications, SMD connectors are used in avionics systems, military communication equipment, and satellite electronics. They must meet strict reliability and performance requirements to ensure the safety and functionality of critical systems.
Choosing the Right SMD Connector
Selecting the appropriate SMD connector for a specific industrial application requires careful consideration of several factors. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
Application Requirements: Understand the specific requirements of your application, including the operating environment, temperature range, vibration levels, and electrical characteristics. This will help you determine the type of connector that is best suited for your needs.
Connector Type and Size: Consider the type and size of the connector based on the number of pins, pitch, and form factor required. Choose a connector that offers the right balance between performance, reliability, and space utilization.
Material and Construction: Look for connectors made from high-quality materials that are resistant to corrosion, wear, and environmental factors. The construction of the connector should also be robust enough to withstand the rigors of industrial use.
Electrical Performance: Ensure that the connector meets the electrical requirements of your application, including voltage rating, current carrying capacity, and signal integrity. Consider factors such as impedance matching, crosstalk, and insertion loss to ensure optimal performance.
Reliability and Durability: In industrial applications, reliability and durability are paramount. Choose connectors that have been tested and proven to withstand harsh operating conditions and provide long-term performance.
Cost and Availability: Consider the cost and availability of the connector when making your selection. Look for connectors that offer a good balance between price and performance, and ensure that they are readily available from reliable suppliers.
Common Issues with SMD Connectors and Troubleshooting Solutions
Despite their many advantages, SMD connectors are not without their challenges. Here are some common issues that may arise and troubleshooting solutions to address them:
Poor Connection: A poor connection can result in intermittent or unreliable performance. This may be caused by factors such as loose contacts, corrosion, or damaged pins. To troubleshoot this issue, check the connector for any signs of damage or wear, and ensure that the contacts are clean and properly seated. If necessary, replace the connector.
Contamination: Contamination of the connector can occur due to dust, dirt, or moisture. This can affect the electrical performance and reliability of the connector. To clean the connector, use a soft brush or compressed air to remove any debris, and then use a suitable cleaning solution to remove any contaminants.
Overheating: Overheating of the connector can occur due to excessive current draw, poor heat dissipation, or high ambient temperatures. This can cause damage to the connector and affect its performance. To prevent overheating, ensure that the connector is properly rated for the application and that there is adequate heat dissipation. If necessary, use a heat sink or other cooling device to dissipate heat.
Vibration and Shock: In industrial applications, connectors may be exposed to vibration and shock, which can cause damage to the connector and affect its performance. To prevent this, use connectors that are designed to withstand vibration and shock, and ensure that they are properly secured to the PCB.
Conclusion
SMD connectors are an essential component in industrial electronics, offering a reliable and efficient connection solution for a wide range of applications. By understanding the different types of SMD connectors, their applications, selection criteria, and potential issues, industrial companies can make informed decisions when choosing the right connector for their needs. With proper selection and installation, SMD connectors can provide long-term performance and reliability, ensuring the smooth operation of industrial equipment and systems.
https://www.sic-components.com/connectors-interconnects
Hot Products
View MoreRelated Blogs

2000+
Daily average RFQ Volume

30,000,000
Standard Product Unit

2800+
Worldwide Manufacturers

15,000 m2
In-stock Warehouse















 Wishlist (0 Items)
Wishlist (0 Items)