
- RFQ
- BOM
-
Contact Us
Tel: +86-0755-83501315
Email: sales@sic-components.com
- Chinese
- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur
Low Noise Amplifier For Medical Devices
In medical electronics, precise acquisition and amplification of weak biological signals are critical for accurate diagnosis and monitoring. Low Noise Amplifiers (LNAs) serve as the front-end building blocks in signal chains, tasked with amplifying tiny signals—such as electrocardiograms (ECGs), electroencephalograms (EEGs), or bioimpedance measurements—while minimizing added noise and distortion. This article explores the role of LNAs in medical devices, their technical requirements, design challenges, and emerging innovations. (https://www.sic-components.com/amplifiers)
Technical Fundamentals of LNAs in Medical Applications
1. Biological Signal Characteristics
Amplitude: Biological signals are extremely low in magnitude:
ECG: 100 µV–5 mV
EEG: 1–100 µV
EMG: 50 µV–20 mV
Frequency Range: Typically low-frequency (DC to 10 kHz for ECG/EEG), making them susceptible to low-frequency noise (e.g., 1/f noise).
2. Noise Sources in Amplifiers
Thermal Noise: Generated by resistive elements (e.g., input resistors), proportional to temperature and bandwidth.
Shot Noise: Arises from random carrier flow in semiconductors (e.g., transistors).
1/f Noise (Flicker Noise): Dominates at low frequencies, caused by surface imperfections in components.
Common-Mode Noise: Interference from power lines (50/60 Hz), electromagnetic interference (EMI), or physiological motion artifacts.
3. Key Performance Metrics
Noise Figure (NF): Measures how much the amplifier degrades the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). For medical LNAs, NF < 3 dB is often required.
Input Referenced Noise (IRN): Combined voltage (e.g., <10 nV/√Hz) and current noise (e.g., <1 pA/√Hz) at the input.
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR): Must be high (≥ 100 dB) to suppress interference in differential measurements (e.g., ECG).
Linearity: Low total harmonic distortion (THD < 0.1%) to preserve signal integrity.
Input Impedance: High (≥ 10 MΩ) to avoid loading biological sources (e.g., skin electrodes).
Applications of LNAs in Medical Devices
1. Electrocardiography (ECG)
Role: Amplify tiny voltage differences between skin electrodes while rejecting muscle artifacts and power-line interference.
Requirement: Differential LNAs with high CMRR (e.g., TI’s OPA1291) and low 1/f noise.
2. Electroencephalography (EEG)
Challenge: Extremely low signals (1–100 µV) require ultra-low noise (e.g., ADI’s AD8232, NF = 1.1 nV/√Hz).
Application: Diagnosing epilepsy, sleep disorders, or brain-computer interfaces (BCIs).
3. Wearable and Implantable Devices
Wearables: LNAs in fitness trackers (e.g., photoplethysmography, PPG) need low power (e.g., Maxim’s MAX4472, 1.6 µA supply current) and small size (SOT-23 ).
Implantables: Sub-microwatt LNAs (e.g., LTC6268 from Analog Devices) for neural recording, with biocompatible packaging.
4. Diagnostic Instruments
Blood Pressure Monitors: Amplify oscillometric signals from pressure sensors, requiring high DC stability.
Lab Equipment: Spectrometers or immunoassay readers use LNAs to amplify photodetector signals (e.g., transimpedance amplifiers for photodiodes).
Design Challenges for Medical LNAs
1. Noise Minimization
Topology: Differential amplifiers reduce common-mode noise; chopper-stabilized or zero-drift amplifiers (e.g., TI’s LTC1050) eliminate 1/f noise.
Component Selection: Low-noise resistors (metal film), decoupling capacitors (ceramic), and low-noise transistors (JFET or CMOS for high input impedance).
2. Power and Size Constraints
Battery-Powered Systems: Prioritize low quiescent current (e.g., LPV811 from TI, 320 nA supply current) for extended runtime in wearables.
Miniaturization: Surface-mount devices (SMD) in compact packages (e.g., QFN, DFN) and integrated signal chains (e.g., AD8233 from ADI, which includes an LNA and filter).
3. Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Resistance
Layout Techniques:
Separate analog and digital ground planes.
Shield sensitive traces (e.g., LNA inputs) with guard rings.
Use ferrite beads to suppress high-frequency noise on power lines.
4. Biocompatibility and Safety
Implantable Devices: LNAs must use hermetically sealed packages (e.g., ceramic) and biocompatible materials (e.g., parylene coatings).
Safety Standards: Compliance with IEC 60601-1 (medical electrical equipment), including isolation requirements for patient-connected circuits.
Key Components and Solutions
Discrete LNAs:
JFET Input Op Amps: Low input current noise (e.g., LT1056 from ADI, IB = 2 pA).
Bipolar Input Op Amps: Low voltage noise (e.g., OP07 from TI, Vn = 10 nV/√Hz).
Integrated Solutions:
BioPotential Amplifiers: AD8232 (ADI) and LTC1864 (TI) integrate LNAs, filters, and voltage references for ECG/EEG.
Low-Power LNAs: LTC6268 (1.8 nV/√Hz, 250 nA current) for battery-powered devices.
Specialized Amplifiers:
Transimpedance Amplifiers (TIAs): For photodiode signals in optical sensors (e.g., TIA1120 from TI, 10^12 Ω input impedance).
Emerging Trends
Zero-Drift and Nanopower Amplifiers:
Innovations like TI’s OPA388 (0.005 µV/°C drift) enable long-term stability without external calibration.
Nanopower designs (e.g., LPV811) extend sensor battery life to 10+ years in IoT devices.
Advanced Fabrication Techniques:
CMOS scaling allows smaller, lower-power LNAs with integrated noise cancellation (e.g., 斩波稳零技术).
AI-Enhanced Signal Processing:
Machine learning algorithms paired with LNAs can dynamically suppress motion artifacts or baseline wander in real time.
Conclusion
Low Noise Amplifiers are indispensable in medical devices, bridging the gap between tiny biological signals and actionable diagnostic information. As medical technology evolves toward miniaturization, portability, and precision, LNAs must continue to balance low noise, low power, and high reliability. Innovations in semiconductor design, integration, and noise cancellation will drive the next generation of medical electronics, enabling more accurate, accessible, and patient-friendly healthcare solutions.
By prioritizing noise reduction, power efficiency, and biocompatibility, engineers can design LNAs that meet the rigorous demands of modern medical applications, from bedside monitors to implantable neural interfaces. As the field progresses, the synergy between analog amplification and digital signal processing will unlock new frontiers in diagnostic accuracy and personalized medicine.
https://www.sic-components.com/amplifiers
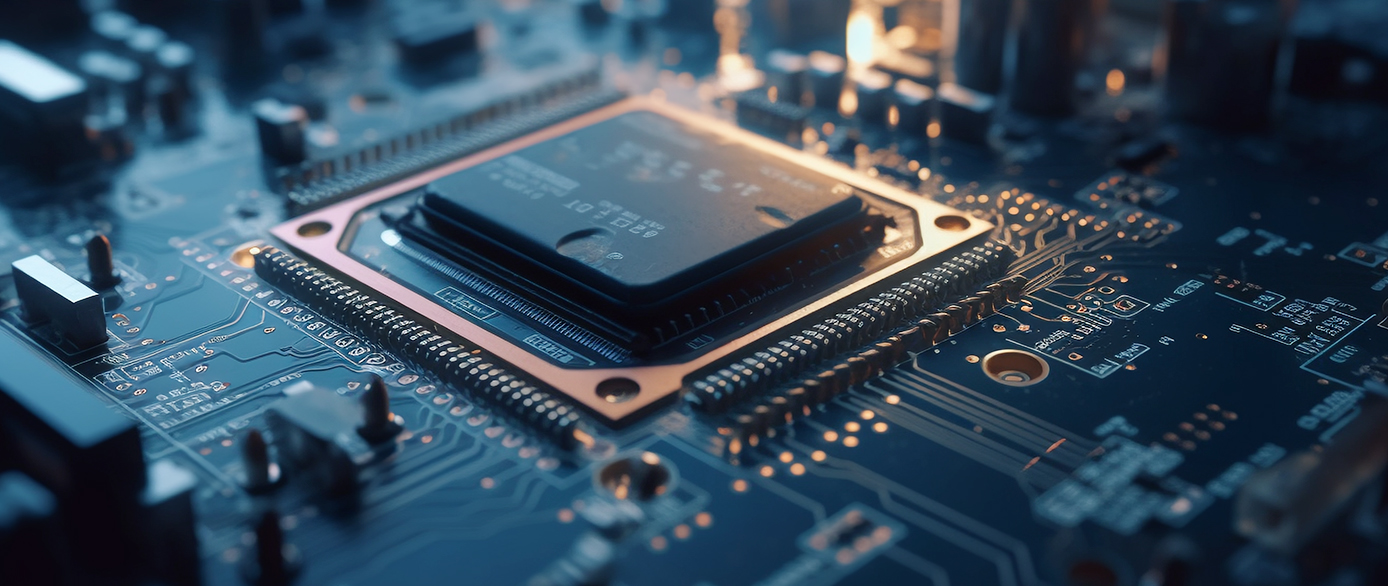
Hot Products
View MoreRelated Blogs

2000+
Daily average RFQ Volume

30,000,000
Standard Product Unit

2800+
Worldwide Manufacturers

15,000 m2
In-stock Warehouse












 Wishlist (0 Items)
Wishlist (0 Items)